RAGFlow System Architecture
Overview
RAGFlow is a fully containerized, micro-service-based RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) engine.
When you run the official docker-compose.yml (or docker-compose-gpu.yml), the following Docker containers are launched automatically:
Core Infrastructure Containers
Container |
Responsibility |
|---|---|
mysql |
Persistent storage for users, knowledge bases, datasets, conversation history, API keys, etc. |
redis |
Cache layer + task queue (Celery) for asynchronous jobs (document parsing, chunking, embedding) |
elasticsearch |
Hybrid search engine: stores text chunks, keyword indices, and (optionally) dense vectors |
minio |
S3-compatible object storage for original uploaded files (PDFs, Word, images, etc.) |
RAGFlow Application Containers
Container |
Responsibility |
|---|---|
ragflow-server (a.k.a. ragflow-api) |
Main FastAPI backend. Exposes all REST endpoints (/api/v1/…) |
ragflow-web |
Frontend (React + Ant Design) – the chat & knowledge-base management UI |
celery-worker (often named ragflow-worker) |
Background workers that execute long-running tasks (DeepDoc parsing, embedding generation, indexing) |
nginx (optional in some setups) |
Reverse proxy / static file server (used in production deployments) |
High-Level Architecture Diagram
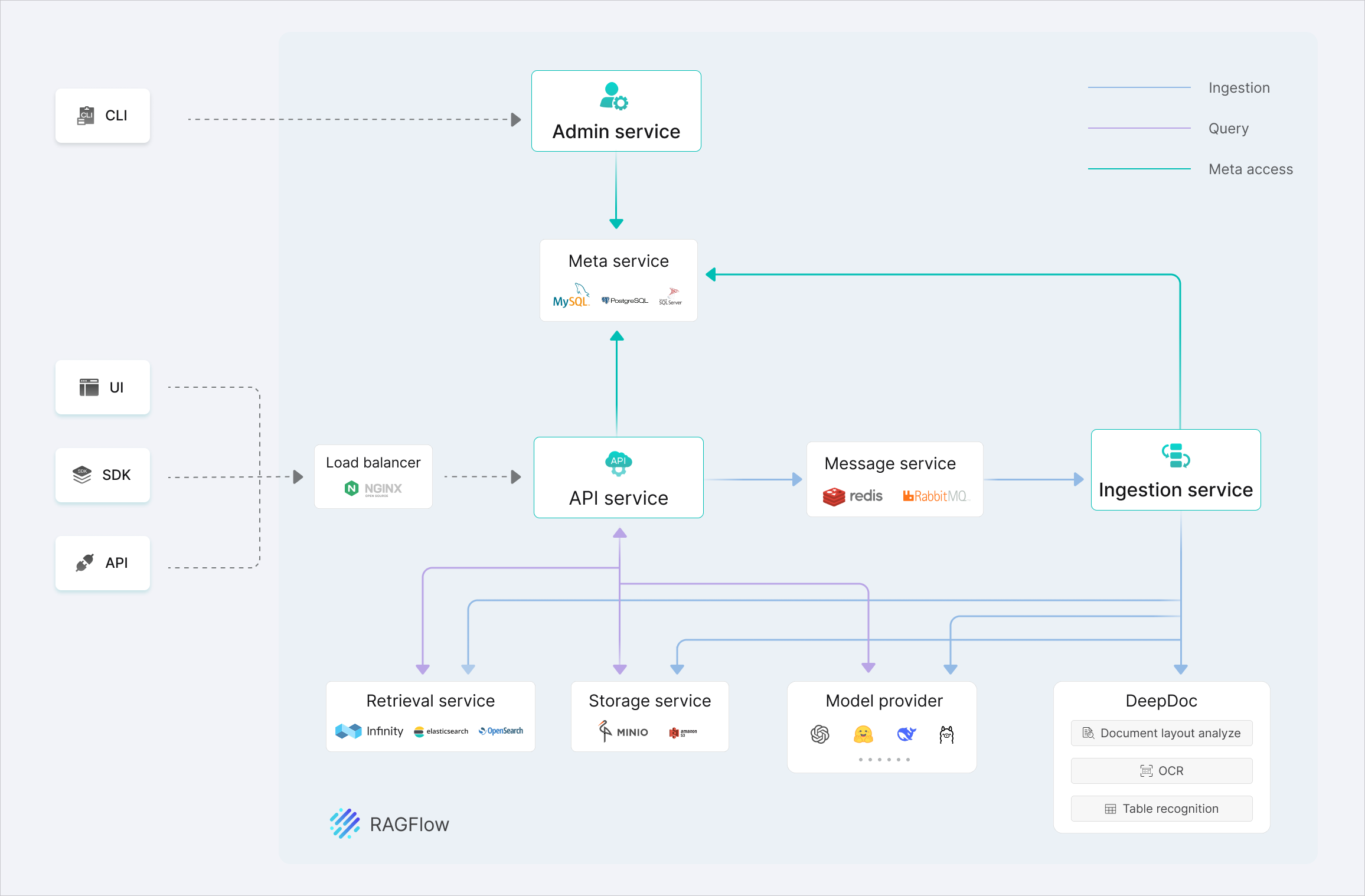
RAGFlow complete system architecture (as of v0.19+, 2025)
Data & Execution Flow
User uploads a document → stored in MinIO → metadata saved in MySQL → parsing task queued in Redis.
Celery worker picks the task → runs DeepDoc (layout detection, OCR, table extraction) → splits into chunks.
Chunks are sent to the configured embedding model (Ollama, vLLM, OpenAI, etc.) → vectors returned.